Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) enables Ethernet transmission via a single pair of wires, ensuring sensor connections are cost-effective, space-saving, and optimized for on-site IP-based communication. Beyond data transmission, Single Pair Ethernet also supports Power over Data Line (PoDL), allowing devices to be powered through the same cable used for data transfer.
SPE meets the requirements for unified network infrastructures, laying the foundation for Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
What is Single Pair Ethernet (SPE)?
Traditional Ethernet has been successful in connecting the upper layers of the automation pyramid, but it’s typically not suitable for the lowest on-site layers due to installation complexity and insufficient maximum transmission distance. This is where Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) significantly extends the capabilities of classic Ethernet.
Single Pair Ethernet is a new physical layer form. Unlike Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps), which requires two wires, or Gigabit Ethernet that needs four wires, Single Pair Ethernet requires only one pair of wires to achieve data transmission. This simplifies the connection of compact devices, sensors, and actuators directly from the field, eliminating the need for additional subsystems or gateways. Thus, SPE is a lightweight and material-saving Ethernet enhancement for many current and future applications.
Future-Proof Network Infrastructure Based on Ethernet Communication
When compared to existing solutions, Ethernet based on TCP/IP and Time-Sensitive Networks (TSN) provides real-time data transmission with significantly higher data rates. For Single Pair Ethernet, this can also be achieved with data coming directly from the field level. Advanced transmission technologies ensure Ethernet communication from sensors to the cloud remains compact and cost-effective. Standardized transmission protocols, wiring, and device components ensure compatibility, making large-scale adoption of SPE in various applications possible.
By using a single or dual pair of wires, existing two-wire cable infrastructure can continue to be used (cable sharing). This greatly reduces material usage, minimizes wiring needs, and facilitates easy integration. The technology is suitable for applications with transmission distances up to 1000 meters, data rates up to 10 Gbps, and power up to 50 W. SPE networks can be set up in star or line topologies, fulfilling the requirements for future-proof network infrastructures.
Key Features of Single Pair Ethernet (SPE)
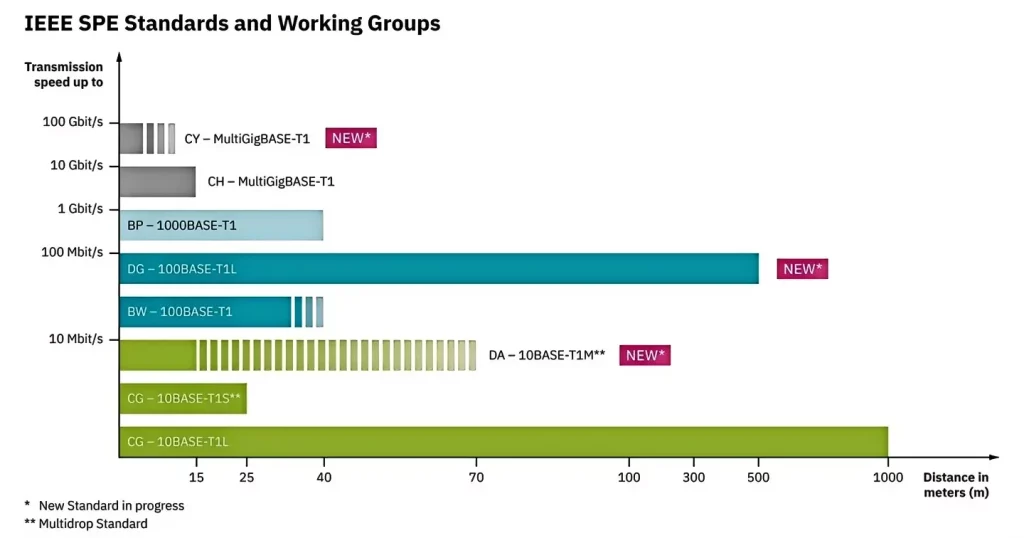
SPE Standards
Various standards and specifications govern the different aspects of SPE technology, including Ethernet interfaces, wiring, and data transmission. The SPE standard is defined in IEEE 802.3, which outlines the framework for Ethernet-based data transmission over a single wire pair. Differences lie in transmission rates and distances. IEC 63171 describes the compatible connectors for these SPE standards.
Transmission Path
Single Pair Ethernet originated in the automotive industry, aiming to create an efficient, unified infrastructure with minimal wiring for high performance. Similar demands apply to applications in other industries. However, in many cases, the 100-meter maximum connection length of classic Ethernet is insufficient. The IEEE 802.3cg standard for 10BASE-T1L in SPE significantly extends the transmission distance, allowing data transmission over 1000 meters.
At a distance of 1000 meters, transmission rates can reach up to 10 Mbps or 1 Gbps, with the distance reducing to 40 meters for higher speeds. Even for the most complex field sensor components, these transmission rates are sufficient, making SPE interfaces ideal for industrial applications.
PoDL — Power over Data Line
In addition to data transmission, SPE technology enables simultaneous power supply to terminal devices. With PoDL (Power over Data Line), up to 50 W of power can be transmitted.
IEEE 802.3bu and IEEE 802.3cg standards define the various performance levels. With this technology, sensors or actuators up to 1000 meters away can be powered through the same cables used for data transmission, minimizing on-site wiring and installation space.
PoDL Performance Categories
| Class | IEEE 802.3bu | IEEE 802.3cg | Units | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 V unregulated | 12 V regulated | 24 V unregulated | 24 V regulated | 48 V regulated | 24 V | 55 V | |||||||||||
| Class # | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
| VPSE(max) | 18 | 36 | 60 | 30 | 58 | V | |||||||||||
| VPSE(min) | 6 | 14,4 | 12 | 26 | 48 | 20 | 50 | V | |||||||||
| IPT(max) | 101 | 227 | 249 | 471 | 97 | 339 | 215 | 461 | 735 | 1360 | 92 | 240 | 632 | 231 | 600 | 1579 | mA |
| PPD(max) | 0,5 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 30 | 50 | 1,23 | 3,2 | 8,3 | 7,7 | 20 | 52 | W |
Applications of Single Pair Ethernet (SPE)
Single Pair Ethernet is ideally suited for a wide range of applications in Industry 4.0, building automation, factory and process automation, and more. SPE technology can be easily integrated into existing Ethernet infrastructures, regardless of the environment. As a space-saving, resource-efficient solution, Single Pair Ethernet provides more room for compact electronic devices by reducing the size of the cables.
Automotive Industry
SPE’s space-saving technology is especially well-suited for applications in the automotive industry. A single twisted pair of wires can achieve data transmission rates from 10 Mbps to 1 Gbps, with a maximum cable length of 15 meters (unshielded) or 40 meters (shielded), making it ideal for automotive wiring harnesses. Furthermore, several new SPE standards are being developed, which are expected to support data transmission rates of up to 10 Gbps or higher. As a result, SPE is set to replace legacy bus systems like CAN, MOST, and FlexRay in next-generation vehicles. Ethernet will unify safety features, control, and communication, forming a prerequisite for connected and autonomous driving.
Industrial Sector
Sensors play a critical role across all manufacturing domains. SPE reliably integrates sensors, actuators, and field devices into existing Ethernet environments, enabling direct transmission of necessary data and process information to the control layer or cloud for analysis. Unlike Fieldbus protocols, Ethernet can be used at every level of automation without the need for additional gateways or interfaces. The reduction to a single wire pair also simplifies sensor wiring in machines or systems, making system construction, operation, and maintenance more efficient and cost-effective.
Process Industry
Ethernet APL can enable direct two-wire Ethernet connections for field devices and sensors in explosion-proof areas of process applications. The Advanced Physical Layer (APL) uses the IEEE 802.3cg 10BASE-T1-L standard along with the IEC TS 60079-47, 2021-03 (2-WISE) standard (2-WISE = Two-Wire Intrinsically Safe Ethernet), supporting explosion-proof methods including intrinsic safety. This allows use in hazardous areas with Ethernet transmission speeds of 10 Mbps over distances of up to 1000 meters. This new communication infrastructure ensures consistent Ethernet usage across process industries.
Building Automation
Connected buildings ensure higher efficiency, increased safety, and added convenience. By using end-to-end IP protocols, devices like sensors, switches, and thermostats can be connected to building management systems through local data networks and the cloud. Consistent SPE wiring replaces existing Fieldbus systems, complex interfaces, and gateways. Existing two-wire cable infrastructure, such as network cables, can also be reused, making installation and commissioning much easier.
SPE Product Overview
Renhotec’s SPE series includes connectors with three different standards:
1. IEC 63171-6 Standard IP20 MICE 1
These connectors are the smallest in terms of plug-in face for building and industrial wiring designs, widely used in smart buildings and industrial environments.
| Product Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |
 |
 |
 |
| No. of Pos | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| P/N | RHT-940000-00-467 | RHT-940000-00-468 | RHT-940000-55-002 | RHT-930000-10-001 |
| Drawing |  |
 |
 |
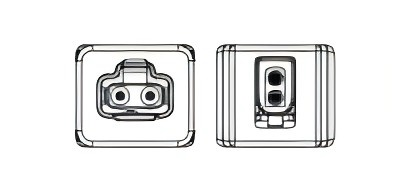 |
| Rated Current | 4A | 4A | 4A | 4A |
| Rated Current | 60v | 60v | 60v | 60v |
| IP Rating | IP20 | IP20 | IP20 | IP20 |
| IEC Standards | IEC 63171-6 | IEC 63171-6 | IEC 63171-6 | IEC 63171-6 |
| Termination | PCB | Crimp | Crimp | Crimp |
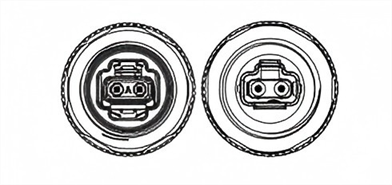
2. IEC 63171-6 Standard IP67 MICE 1/2/3
The M8 hybrid connectors are specifically designed for field wiring and sensor connections, supporting PoDL (Power over Data Line), and compliant with IEEE 802.3bu/cg standards. These are ideal for industrial environments.
| Product Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |
 |
 |
| No. of Pos | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| P/N | RHT-080004-05-001 RHT-080004-06-001 |
RHT-080004-03-001 RHT-080004-04-001 |
RHT-080004-01-001 RHT-080004-02-001 |
| Drawing | 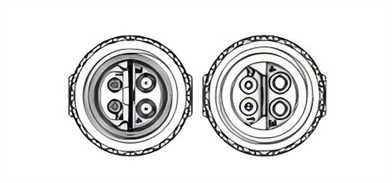 |
 |
 |
| Rated Current | 4A/8A | 4A/8A | 4A |
| Rated Current | 60v | 60v | 60v |
| IP Rating | IP67 | IP67 | IP67 |
| IEC Standards | IEC 63171-6 | IEC 63171-6 | IEC 63171-6 |
| Termination | – | PCB Solder | Crimp |
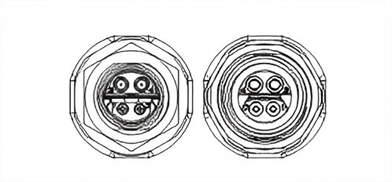
3. IEC 63171-7 Standard IP67 MICE 1/2/3
The M12 hybrid connectors enable both data and power transmission via a single wire pair. These connectors integrate data and additional power contacts, supporting up to 63V DC and 8A current, and are widely used across various industrial sectors.
| Product Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |
 |
 |
| No. of Pos | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| P/N | RHT-121507-03-001 RHT-121507-04-001 |
RHT-121507-03-002 RHT-121507-04-002 |
RHT-121507-05-001 RHT-121507-06-001 |
| Drawing |  |
 |
 |
| Rated Current | 2A/8A | 2A/8A | 2A/8A |
| Rated Current | 50AC/63DC | 50AC/63DC | 50AC/63DC |
| IP Rating | IP67 | IP67 | IP67 |
| IEC Standards | IEC 63171-7 | IEC 63171-7 | IEC 63171-7 |
| Termination | PCB Solder | PCB Solder | – |
Conclusion
Ethernet technology has made significant advancements in speed, reliability, and application range in recent years, particularly with the widespread adoption of 10GbE, 25GbE, and higher bandwidth standards, which have driven the growth of data centers, edge computing, and smart buildings. In the future, with the development of 5G, AI, and the Internet of Things (IoT), Ethernet will continue to play a key role in supporting ultra-fast data transmission, low-latency networks, and higher energy efficiency. The development of technologies like Power over Ethernet (PoE) will also facilitate Ethernet’s application in smart buildings and industrial automation, laying the foundation for a connected future.
Similarly, Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) technology has rapidly evolved in recent years, becoming a key enabler in industries such as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), automotive, and smart buildings. SPE transmits data and power over a single pair of copper wires, simplifying wiring structures, reducing costs, and enhancing device connectivity flexibility. Its low power consumption and long transmission distances make it particularly suitable for connecting low-bandwidth devices such as sensors and controllers. In the future, SPE is expected to play a crucial role in smart manufacturing, autonomous driving, and broader IoT applications, driving the development of the interconnected world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What transmission speeds are supported by SPE?
Current Ethernet technologies can provide transmission speeds of up to 10 Gbps using just one pair of wires for applications.
2. Why should you use SPE?
With the SPE infrastructure, data wiring can be reduced, preventing media failures and device faults from the field to the cloud. Additionally, a consistent Ethernet structure can be established, eliminating the need for gateways. Moreover, SPE wiring is simpler and more time-efficient because only two wires need to be connected. The 10Base-T1L standard supports Ethernet wiring with a range of up to 1000 meters.
3. What are the standards for SPE?
SPE standards are defined in IEEE 802.3. There are currently five different standards, each with varying transmission speeds and distances. Additional standards are under discussion.
4. Does SPE support power transmission?
Yes, through the PoDL (Power over Data Line) standard, it can transmit up to 50 W of power. Various performance levels are described in the IEEE 802.3bu and IEEE 802.3cg standards.
5. What should be done with existing cable infrastructure?
If the existing cable infrastructure meets the requirements, it can be used for SPE. SPE cables are defined in the IEC 61156-1x standard.